Supercharge Your Workout – The Ultimate Guide to Creatine and Its Dynamic Duos
Creatine is a term that almost every fitness enthusiast and…
Creatine is a term that almost every fitness enthusiast and bodybuilder has heard. Often surrounded by myths and misconceptions, creatine has earned its reputation as a powerhouse supplement—but what exactly is it, and how can you harness its benefits? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on an insightful journey into the world of creatine. We’ll break down the science behind its natural occurrence, explore its critical role in energy production and muscle growth, delve into its cognitive perks, and review the various forms available on the market. Whether you’re new to supplementation or looking to optimize your routine, this article will help you separate fact from fiction and use creatine to supercharge your performance.
What Is Creatine? The Science and Natural Occurrence
At its core, creatine is a naturally occurring molecule synthesized from three amino acids: glycine, arginine, and methionine. Your body produces creatine primarily in the liver and kidneys. Once formed, creatine travels through your bloodstream and is stored in your muscles—about 95% of your body’s creatine is tucked away as phosphocreatine.
Nature’s Energy Booster
Not only is creatine produced by your body, but it is also present in dietary sources—most notably in meat and fish. This is why vegetarians and vegans often consider supplementation: without meat as a regular part of their diet, they may have lower creatine levels. However, regardless of how you obtain it, creatine plays a pivotal role in powering your workouts and everyday activities.
Energy Production – The ATP-Phosphocreatine System
One of creatine’s most celebrated roles is its ability to rapidly regenerate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the body’s primary energy currency.
How It Works
During high-intensity, short-duration activities—like sprinting, weightlifting, or explosive sports—your muscles rely on ATP for quick bursts of energy. However, ATP stores are limited and deplete rapidly. This is where creatine comes in. Stored as phosphocreatine in your muscles, creatine donates a phosphate group to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) to quickly replenish ATP levels. This process, known as the ATP-phosphocreatine system, allows you to sustain peak performance during those crucial moments of high-intensity activity.
Real-World Benefits
Imagine you’re in the middle of a heavy lifting session or sprinting for that extra few seconds in a race. With creatine on board, your muscles can recover ATP more rapidly, meaning you might experience enhanced power, improved endurance, and the ability to push through those extra reps or seconds. This rapid regeneration of energy is one of the key reasons creatine is revered by athletes and bodybuilders alike.
Muscle Growth and Recovery
Beyond energy production, creatine plays an essential role in muscle growth and recovery—two factors that are crucial for anyone serious about fitness.
Increasing Water Content in Muscles
When you supplement with creatine, one of the immediate effects is an increase in water content within your muscle cells. This isn’t just about looking fuller—cellular hydration is vital for muscle function and protein synthesis. Better-hydrated muscle cells are more efficient at recovering from strenuous exercise and building new muscle tissue.
Boosting Growth-Related Hormones
Creatine supplementation has been shown to elevate levels of certain growth factors and hormones that are key to muscle hypertrophy. By creating an environment conducive to muscle repair and growth, creatine allows you to train harder and recover faster, ultimately leading to improved muscle mass over time.
Enhancing Recovery
Faster recovery means you can train more consistently. Whether you’re a bodybuilder aiming for greater muscle volume or an athlete looking to bounce back quickly between intense training sessions, creatine helps reduce muscle fatigue and soreness, letting you push your limits safely and effectively.
Cognitive Benefits – Not Just Muscle Power
While creatine’s impact on physical performance is well-documented, emerging research suggests that its benefits extend to the brain as well.
Brain Energy Boost
Just like muscles, your brain relies on ATP to function optimally. Creatine supports ATP regeneration in neural tissue, which can help enhance cognitive performance. This may translate into better focus, improved short-term memory, and faster mental processing—benefits that are particularly noticeable during periods of sleep deprivation or intense mental activity.
Neuroprotection and Cognitive Enhancement
Some studies indicate that creatine may have neuroprotective properties, potentially helping to guard against neurological disorders. Although research in this area is still in its early stages, the evidence is promising. For vegetarians and vegans—whose diets might provide less dietary creatine—the cognitive boost from supplementation can be especially beneficial.
Exploring Creatine Types
The supplement market offers several forms of creatine, each with its own set of advantages and potential drawbacks. Let’s break down the most popular types so you can decide which might work best for you.
Creatine Monohydrate
Description:
Creatine monohydrate is the quintessential form of creatine. In this compound, creatine is bound with a water molecule, making it one of the most studied and widely used forms.
Advantages:
- Extensive Research: Backed by decades of research, creatine monohydrate is proven to be effective.
- Cost-Effective: It’s one of the most affordable forms of creatine on the market.
- High Efficacy: Many athletes and bodybuilders swear by it for boosting strength and muscle growth.
Potential Side Effects:
- Solubility Issues: Some users may experience gastrointestinal discomfort such as bloating, cramping, or diarrhea if the powder does not dissolve completely.
- Water Retention: Weight gain from creatine is typically due to water retention in muscle cells, not fat accumulation.
Creatine Hydrochloride (HCL)
Description:
In creatine hydrochloride, creatine is bound to a hydrochloride group, significantly enhancing its solubility in water.
Advantages:
- Improved Absorption: Its high solubility may lead to better absorption and reduced risk of gastrointestinal discomfort compared to creatine monohydrate.
- Lower Dosage: Some users find they need less of it to achieve the desired benefits.
Potential Side Effects:
- Newer on the Market: Although promising, long-term studies on creatine HCL are fewer than those on creatine monohydrate, so its long-term side effects aren’t as thoroughly documented.
Creatine Ethyl Ester (CEE)
Description:
Creatine ethyl ester is a form of creatine attached to an ester, which is intended to improve its absorption into the bloodstream.
Advantages:
- Potential for Enhanced Absorption: Some proponents suggest that CEE may be absorbed more efficiently, meaning less creatine is wasted.
Potential Side Effects:
- Rapid Breakdown: Some research indicates that CEE may break down into creatinine—a waste product—more rapidly than other forms, potentially reducing its overall efficacy.
- Taste and Gastrointestinal Issues: Users sometimes report an unpleasant taste, and if not properly dissolved, it may cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
Turbo-Charge Your Creatine – The Beta-Alanine Boost
For those looking to maximize athletic performance, combining creatine with other supplements can create a synergistic effect. One powerful combination is creatine with beta-alanine.
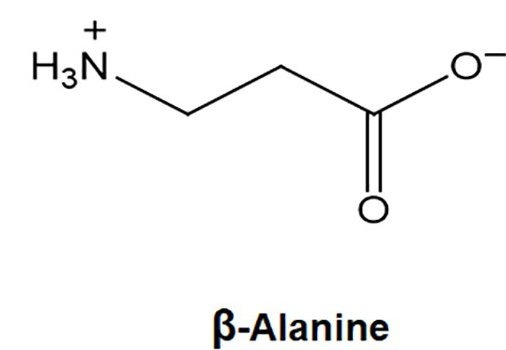
What Is Beta-Alanine?
Beta-alanine is a non-essential amino acid that, once ingested, converts into carnosine. Carnosine acts as a buffer in muscle cells, helping to reduce acid buildup during high-intensity exercise. This buffering capacity can delay fatigue and improve overall performance.
Why Pair Creatine and Beta-Alanine?
- Amplified Workout Volume: Creatine fuels your muscles for short bursts of energy, while beta-alanine helps stave off fatigue during extended efforts. Together, they allow you to push harder and for longer periods.
- Enhanced Endurance: Beta-alanine is particularly effective in aerobic and endurance activities, complementing creatine’s strength-building properties.
- Synergistic Muscle Growth: By enabling higher training volumes and reducing fatigue, this dynamic duo indirectly supports greater muscle hypertrophy over time.
The Ultimate Performance Trio – Creatine, Beta-Alanine, & L-Citrulline
Taking your supplementation game a step further, some athletes incorporate L-citrulline into their regimen. L-citrulline is an amino acid that converts into L-arginine in your body, leading to increased nitric oxide production—a molecule that plays a key role in blood vessel dilation.
Why Consider L-Citrulline?
- Enhanced Nutrient Delivery: With improved blood flow from nitric oxide, your muscles receive creatine and other nutrients more efficiently. This can boost both energy and recovery.
- Delaying Muscle Fatigue: L-citrulline can help delay the onset of fatigue by ensuring your muscles receive an adequate supply of oxygen during intense exercise.
- Accelerated Recovery: Better blood flow also means that metabolic waste products are removed more quickly, aiding in faster recovery after workouts.
Crafting Your Personalized Pre-Workout Potion
Now that you understand the science and benefits behind creatine, beta-alanine, and L-citrulline, it’s time to think about how to create your own personalized pre-workout blend. This isn’t just about mixing supplements—it’s about curating a formula that caters specifically to your workout needs, training intensity, and recovery goals.
Consider Your Goals
- Strength and Power: If your focus is on explosive strength and powerlifting, a creatine-heavy formula might be best. Creatine monohydrate remains a solid choice for rapid ATP regeneration and muscle hydration.
- Endurance and Stamina: For endurance athletes, adding beta-alanine and L-citrulline can help delay fatigue and enhance oxygen delivery to muscles, ensuring you perform at your best for longer.
- Balanced Performance: Many athletes find that a well-rounded mix of 3-5 grams of creatine, 2-5 grams of beta-alanine, and 2-3 grams of L-citrulline before training offers an optimal blend of strength, endurance, and rapid recovery.
Experiment and Monitor
Every individual is unique. It’s important to experiment with different dosages and combinations to see what works best for your body. Keeping a training journal to track how you feel during and after workouts can be incredibly helpful. Over time, you’ll be able to fine-tune your pre-workout potion so that it perfectly aligns with your performance goals.
The Loading Phase – Kickstarting Your Creatine Journey
Many athletes choose to begin creatine supplementation with a “loading phase” to rapidly saturate their muscles with creatine. This phase typically involves taking a higher dose of creatine for about a week before transitioning to a maintenance dose.
How the Loading Phase Works
- Dosage Strategy: The loading phase usually involves consuming around 20 grams of creatine per day, divided into 4–5 smaller doses. This approach quickly increases the creatine stores in your muscles.
- Transition to Maintenance: After the loading phase, most people shift to a daily maintenance dose of 3-5 grams. This helps keep your muscles saturated without the need for high daily doses.
Direct Maintenance Option
While the loading phase is effective, it isn’t mandatory. Many athletes opt to start directly with the maintenance dose, gradually building up muscle saturation over time. This approach can help avoid potential side effects like gastrointestinal discomfort, while still delivering the long-term benefits of creatine supplementation.
Busting Myths and Misconceptions
Despite the wealth of scientific research supporting creatine’s benefits, myths and misconceptions continue to circulate. Let’s clear up a few common ones:
Myth 1: Creatine Is a Steroid
Creatine is not a steroid. It is a naturally occurring compound that works by enhancing your body’s ability to regenerate ATP—not by altering your hormone levels. The weight gain often associated with creatine is primarily due to increased water retention in muscle cells, not fat gain.
Myth 2: Creatine Harms the Kidneys
There has been some concern that creatine supplementation might stress the kidneys. However, for healthy individuals, research has not demonstrated any significant kidney damage from standard dosages of creatine. The key here is hydration—ensuring you drink plenty of water is essential when taking creatine, as increased creatine levels also raise your hydration needs.
The Importance of Hydration
Proper hydration is integral when supplementing with creatine. Since creatine draws water into muscle cells, failing to drink enough fluids can lead to dehydration and, in extreme cases, place undue stress on the kidneys. Always aim to increase your water intake when you start a creatine regimen.
Caveats and Considerations
While creatine is one of the most researched and effective supplements on the market, it’s important to remember that everyone’s body is unique. Here are a few considerations to keep in mind:
- Individual Responses Vary: Not everyone experiences the same level of benefit from creatine supplementation. Some individuals may notice dramatic improvements in performance, while others may experience more modest gains.
- Quality Matters: Choose high-quality supplements from reputable brands to ensure purity and efficacy.
- Dosage Is Key: Stick to recommended dosages—typically 3-5 grams per day during maintenance—and adjust as needed based on your training intensity and body response.
- Consult a Professional: If you have any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns, consult with a healthcare professional or sports nutritionist before beginning supplementation.
Conclusion: Optimize Your Performance with Creatine
Creatine is far more than a buzzword among bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts—it’s a dynamic, multifaceted supplement with benefits that span from muscle strength and recovery to cognitive enhancement. By understanding its natural occurrence, the science behind the ATP-phosphocreatine system, and the various forms available on the market, you can make informed decisions that optimize your training regimen.
Whether you’re just starting your fitness journey or you’re a seasoned athlete looking to fine-tune your performance, creatine offers a proven way to push your limits and achieve your goals. From the classic creatine monohydrate to newer variants like creatine HCL and CEE, and when combined with performance-enhancing allies like beta-alanine and L-citrulline, creatine can become a key component of your personalized pre-workout potion.
Remember: stay hydrated, start with the right dosage, and listen to your body. With these guidelines in mind, you’ll be well on your way to unlocking the full potential of creatine—fuelling your workouts, boosting recovery, and perhaps even enhancing your mental performance.
Disclaimer: This blog post is crafted for informational purposes and isn’t an endorsement of any supplements. Consultation with professionals is vital when making health or athletic decisions.